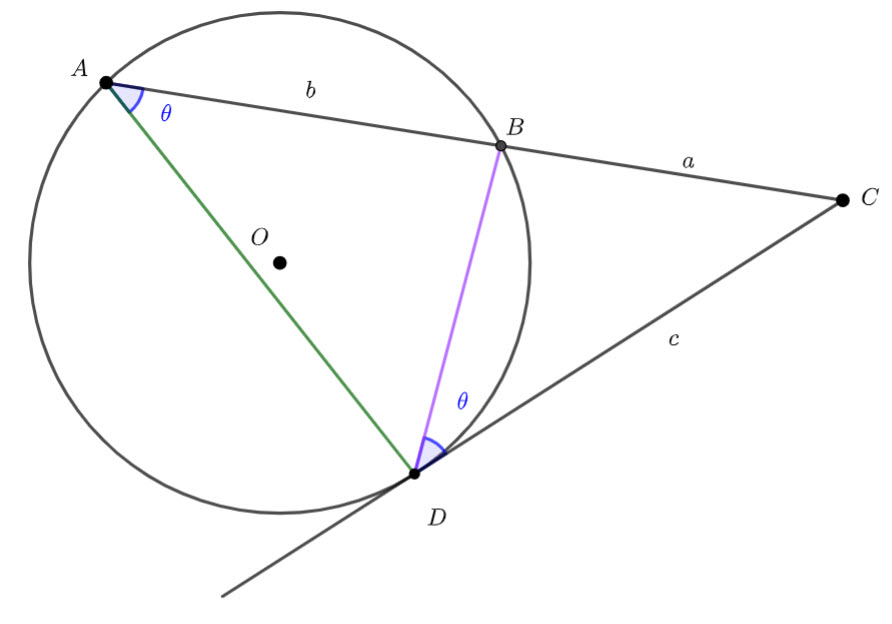
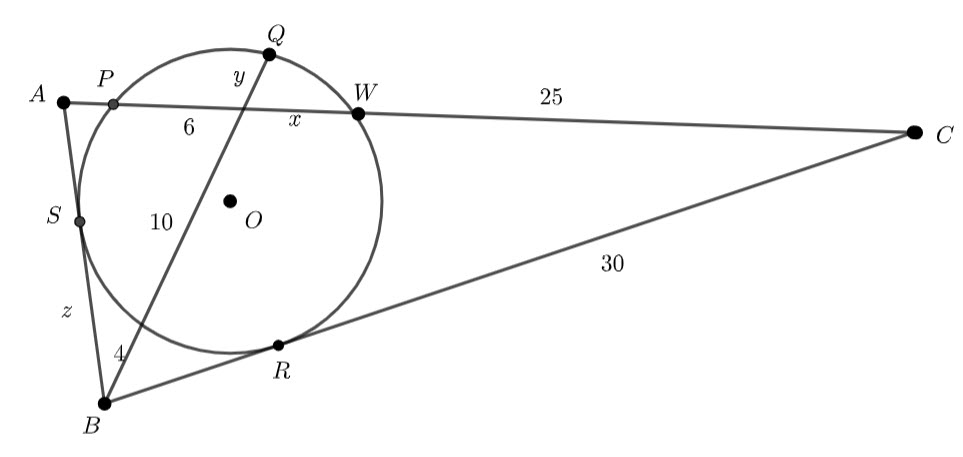
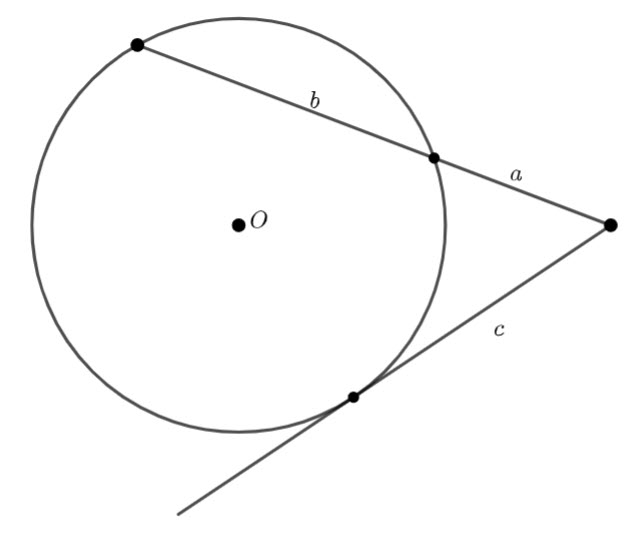
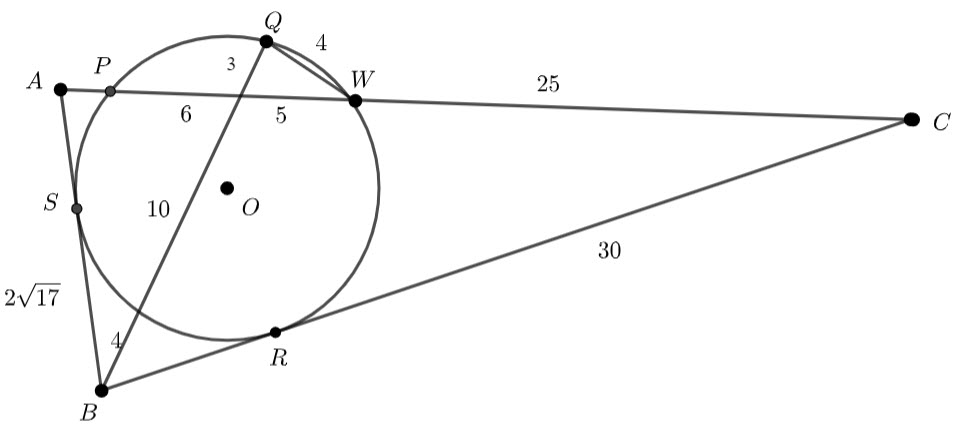
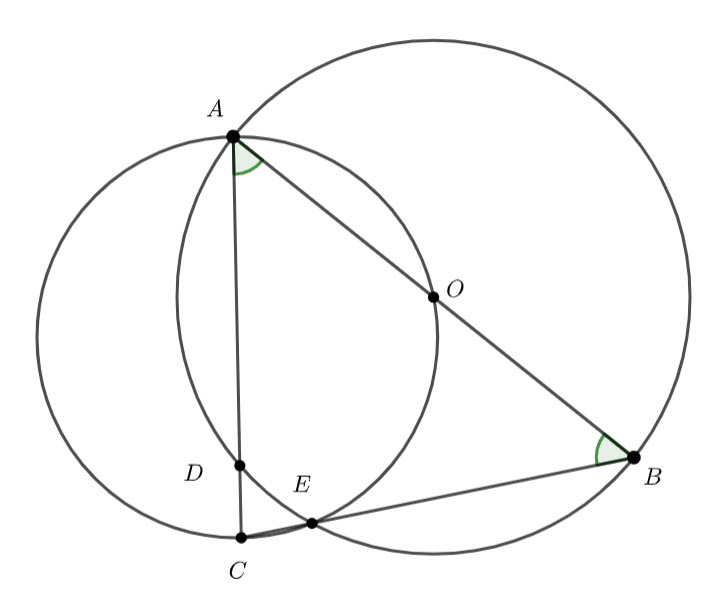
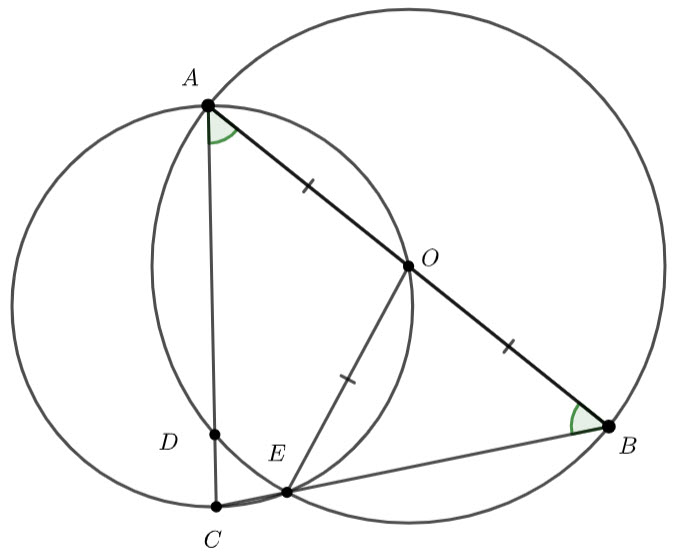
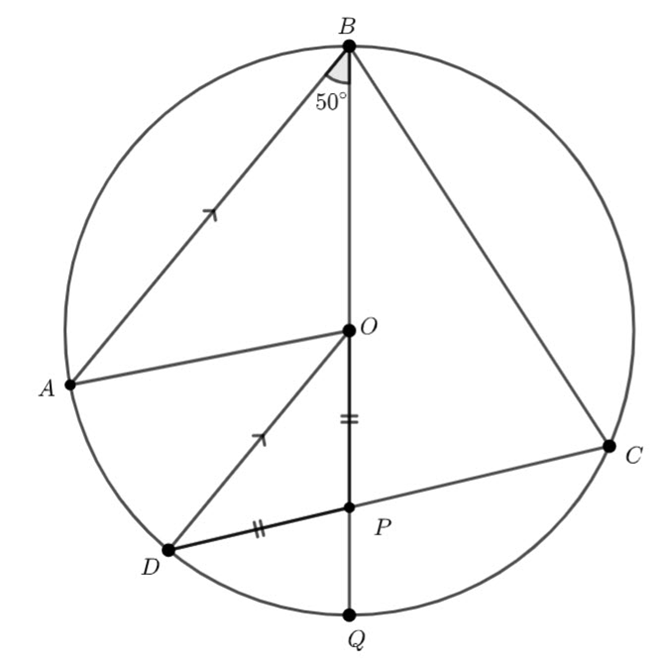
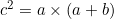In the diagram below, ![]() and
and ![]() lie on the circle with centre
lie on the circle with centre ![]() . If
. If ![]() and
and ![]() , determine with reasoning
, determine with reasoning ![]() and
and ![]()

We know ![]() – radii of the circle.
– radii of the circle.
Which means, ![]() is isosceles and
is isosceles and ![]() – equal angles isosceles triangle.
– equal angles isosceles triangle.
![]() – angle at the centre twice the angle at the circumference.
– angle at the centre twice the angle at the circumference.
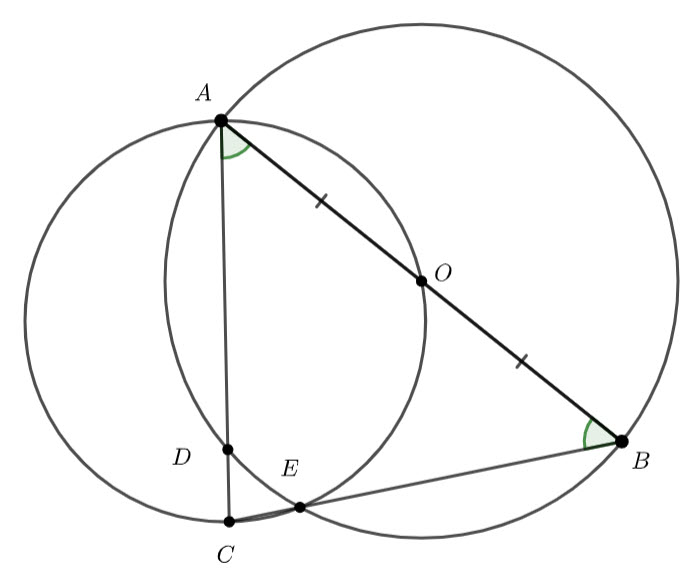
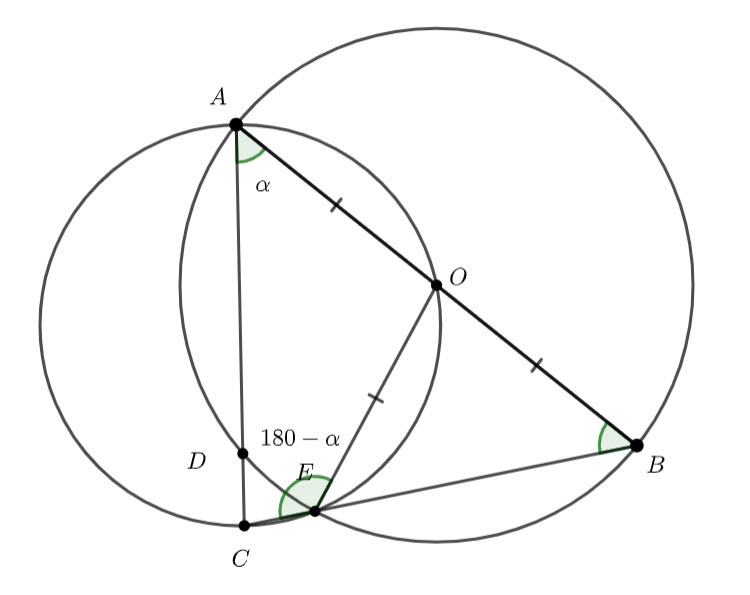
![]()

This means ![]() – angles on a straight line are supplementary
– angles on a straight line are supplementary
![]() – equal angles isosceles triangle and the angle sum of a triangle.
– equal angles isosceles triangle and the angle sum of a triangle.
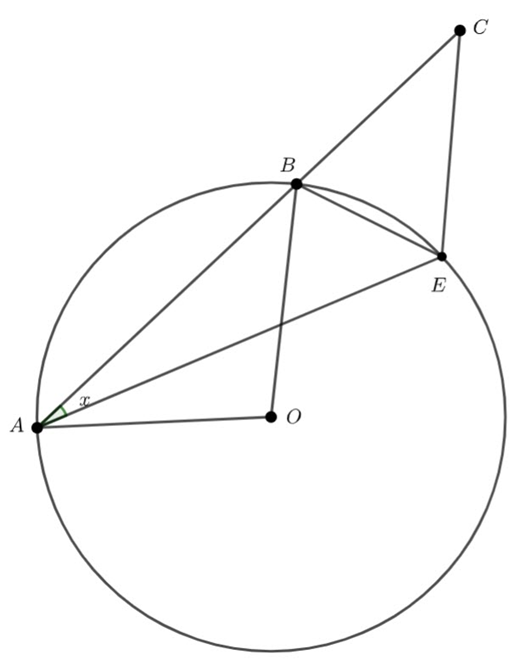
![]() – angle at the circumference subtended by the same arc are congruent.
– angle at the circumference subtended by the same arc are congruent.

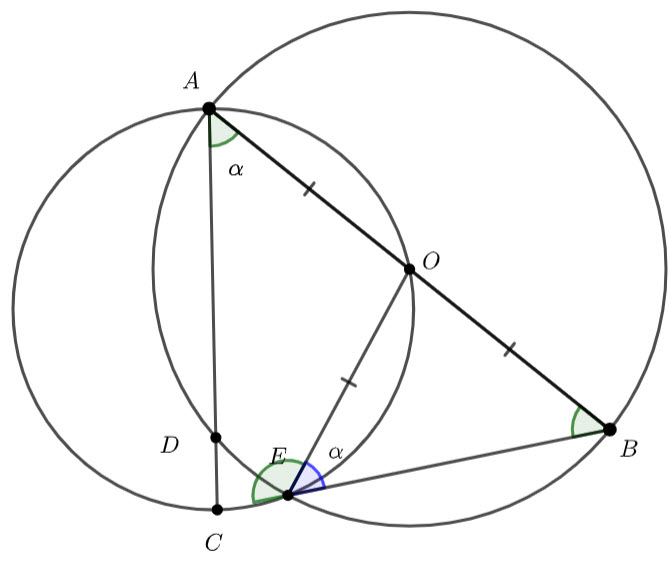
![]() – angles at the circumference subtended by the same arc are congruent.
– angles at the circumference subtended by the same arc are congruent.
![]() – equal angle isosceles triangle
– equal angle isosceles triangle
Hence ![]()
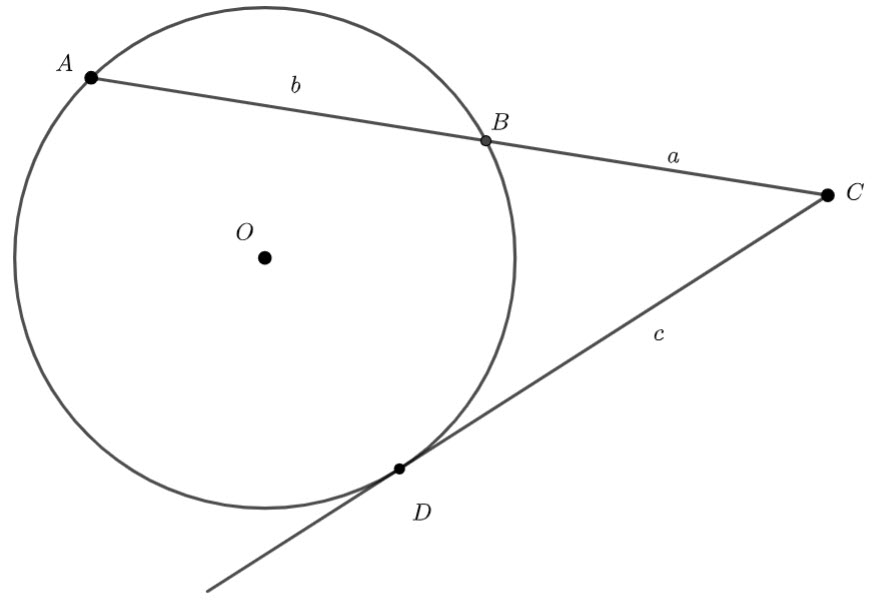
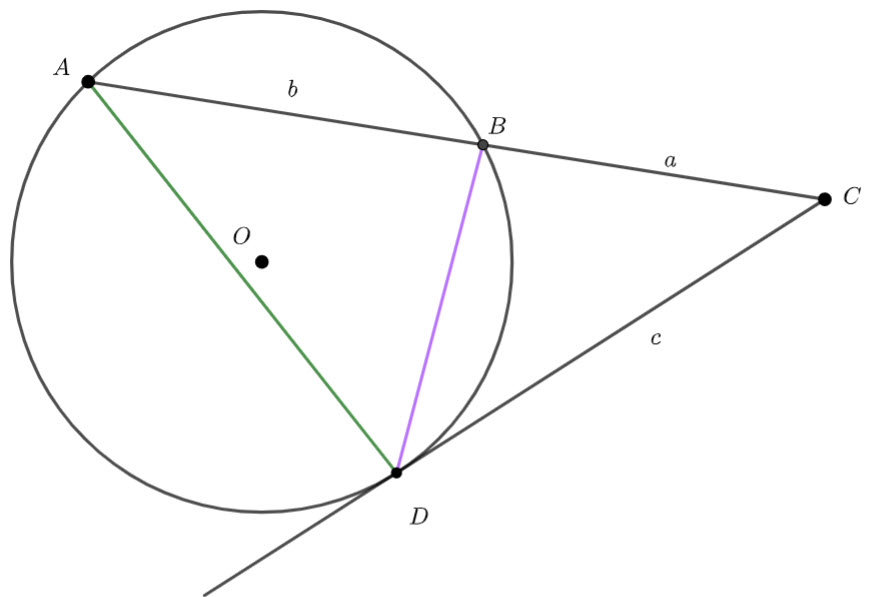
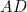 and
and 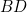 are added
are added